
These techniques are also used for other variants with constraints over combinations: (non)-consecutive, square wisdom, ratio, bossdoku, renban...
The regular naked subset may be extended to killer sudoku where we may consider cages as 'entities' just like cells. These entities forms Almost Locked Sets (ALS) depending their combinations.
In this first example, the cage 5/2 can be either {14} or {23}. Whichever the case, it must include either a 1 or a 2. This forms a complex naked pair with the cell at its left : Either the cell is 1 and the cage is {23} or the cell is 2 and the cage {14}. Whichever the case, both 1 and 2 are locked in these 3 cells. Therefore, no other cell of the row or nonet may have {12}.

In this second example, two cages forms a complex naked pair in R1. Cage 15/3 in R1C123 and cage 11/2 in R1C45.

Using Show Combinations may also help you spot such complex naked pairs. Here are the infos of the two cages:
Cage 15/3 at R1C1 = {168|249|267|348}
It must have at least one of {28|46}
It cannot have {5}
It cannot have both {12|13|14|17|19|23|28|36|37|39|46|47|69|78|79|89}
Cage 11/2 at R1C4 = {29|38}
It must have at least one of {23|28|39|89}
It cannot have {14567}
It cannot have both {23|28|39|89}
This reveals that Cage 15/3 at R1C1 must have at least one of {28} as do Cage 11/2 at R1C4. Therefore, no other cell of R1 may have {28}.
Hint: for cages with 2 cells and 2 possible combinations, you can easilly see the possible combinations and the 'must have at least one of' pairs by examing their pencil marks. For instance, the cells in the cage 11/2 have 4 possibilities {2389} displayed in a square. The possible combinations are at opposite diagonals, connected like an X: {29} or {38}. The 'must have at least one of' pairs are at the sides of the square formed by the pencil marks: {23} or {28} or {39} or {89}.
Here is an example of a complex naked triplet. Three 'entities' forms a naked triplet: two cells R9C12 and cage 8/2 at R9C56. The cage 8/3 can be {17} or {26} or {35}, so it must include either 1, 2 or 3, as do the two cells at R9C12. Therefore, no other cell of R9 may have {123}.

Other ALS may be used to form complex naked subsets. For example, one 'entity' may be replaced by a UR type 3.
Note: This solver currently only implements the case of complex naked pairs & triplets. It will not find complex naked quads, quints...
The regular hidden subset may be extended to killer sudoku where we may consider cages as 'entities' just like cells. In this example, the possibilities {79} of R9 are locked in R9C124. There are only two 'entities' in R9 which may contain {79}: the cage 12/2 in R9C12 and the cell at R9C4. Since none the these entities may include both {79}, each of them must include one of {79}. Therefore R9C4 is limited to {79}.

This solver will detect cages with conflicting combinations, that is combinations which would cancel every possibilities of another cell or some other cage.
In this first example, the cage 14/2 cannot be {68} since it would cancel every possibility for the cell at the left. Therefore the cage 14/2 must be {59}.

In this second example, the cage 10/2 at R2C12 cannot be {28} nor {46} since the cage 15/3 in R1C123 must have at least one of {28} and also one of {46}. Therefore the cage 10/2 is {19} or {37}

The cage may also conflict with other ALS. For example, one 'entity' may be replaced by a UR type 3. See also my article on Uniqueness techniques for Killer.
Note: This solver currently only checks for cages conflicting with a cell with two possibilities or a cage having a mandatory alternative pair of possibilities. It will also check for combinations conflicting with a cell with three possibilities or another cage which must include at least one out of three possibilities It will not check conflicts with four or more possibilities.
This solver searches for some candidate for some house locked in two cages and consider the possibles combinations. It searches for another candidate also locked in one of the two cages.
In this example the 4 of R1 is locked in R1C1256, which are within two cages 12/2 -> one of the cage must be {48} -> 8 of R1 is also locked in one of these cages.
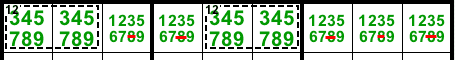
In this example the 1 of R1 is locked in R1C12456, either in cage 8/2={17} or cage 17/3={179} -> 7 of R1 is also locked in one of these cages.

In this example the 4 of R1 is locked in R1C124, which are within two cages 12/2 -> either cage 12/2 in R1C12 = {48} or cage 12/2 in R12C4 = [48] -> 8 locked in R1C12 or R2C4 -> R1C456 & R2C123 <> 8. This is similar to Y-Wing.

This is like Grouped XY-Chain & Loop, but will also search for chains using XY links through cages.
Examples to come. See also my post Chains & loops for Killer using AIC
This solver checks combinations of two adjacent or overlapping cages together. This is last in the list since it does not give the logical reasons for the eliminations. So you’ll have to findout the logic yourself. Nevertheless, it could help spotting areas of interset, where eliminations can be made.
Examples to come.
Simple Techniques | Fishes & Single Digit | Wings | XY-Chains, Loops & ALS | Uniqueness | Jigsaw, Windoku & Gatai | Greater/Less Than & Non-Consecutive | Killer | Innies/Outies | Advanced Killer | Square Wisdom | Contents
Copyright (C) 2006-2008 Jean-Christophe Godart. All rights reserved.